Hall of Fame Model
Table of ContentsClose
1 Activating Python Environment
This code block must be run to activate python virtual environment for org session "SESSION_1". The following Python code blocks are run in "SESSION_1" in which the virtual environment should have been activated.
(pyvenv-activate "~/gitRepos/TTK28-project/venv/")
2 Importing Dependencies
This project is primarily uses Keras and Sklearn for the data analysis
itself. For data storage and manipulation pandas and numpy are the primary
libraries used. The graphics are generated via matplotlib.
from datetime import datetime import pandas as pd import numpy as np import matplotlib matplotlib.use('PS') import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import logging from sklearn import tree, decomposition from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, roc_curve, roc_auc_score, accuracy_score, auc, matthews_corrcoef, make_scorer from sklearn.utils import class_weight from sklearn.model_selection import KFold, StratifiedKFold, cross_val_score, cross_validate, learning_curve from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV import scikitplot as skplt import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow import keras from tensorflow.keras import Model from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import CSVLogger, ModelCheckpoint from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential, model_from_json, load_model from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense from tensorflow.keras.wrappers.scikit_learn import KerasClassifier
3 Hyperparameters
In order to more easily configure the model and keep track of the settting, this hyperparameters dictionary is defined here and used throughout the code where needed.
HP = { 'NAME': 'full', 'INFO': 'checking_testing_final', 'EPOCHS': 50, 'FOLDS': 2, 'BATCH_SIZE': 1, 'OPTIMIZER': 'adam', 'LOSS': 'binary_crossentropy', 'METRICS': ['accuracy', 'Recall'], 'DATASET': 'raw' }
4 Logging Setup
It was quite hard to keep track of different runs in the project, and noticed I kept loosing track of previous runs and just wanted a log to save some of the metrics and information about the different runs.
4.1 Simply adding whitespace to log file
Nothing special is happening here, but just making sure there is whitespace between runs in the log file.
with open("../result/master_log.txt", "a") as file: file.write("\n") file.write("\n") print(HP, file=file)
4.2 Defining CSVLogger and Tensorboard Settings
CSVLogger is used to keep track of the different runs manually, in addition to setting up tensorboard.
csv_logger = CSVLogger('../result/master_log.txt', append=True, separator=';') log_dir = "../logs/scalars/" + datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d-%H%M%S") tensorboard_callback = keras.callbacks.TensorBoard(log_dir=log_dir)
4.3 STDOUT Logging Settings
These are the settings for logging information to the terminal and debugging the output.
# logging.basicConfig(encoding='utf-8', level=logging.INFO)
5 Defining Helper Functions
5.1 Creating an ROC Plot
This is a plot that takes in the "false positives" (fper) and "true
positives" (tper) and the name of which to save the plot. It generates,
shows, and saves an Receiver Operator Characteristics plot which is used
for binary classifications problems. A good explanation can be found here.
def plot_roc_curve(fper, tper, name): plt.plot(fper, tper, color='orange', label='ROC') plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], color='darkblue', linestyle='--') plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate') plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate') plt.title('Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve') plt.legend() file_name = '../result/ROC_curve_' + name + datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d-%H%M%S") + '.png' plt.savefig(file_name) plt.savefig("../result/ROC_curve_latest.png")
5.2 Saving and Loading Models
Simply functions to save and load varieties of this hof_model.
def save_model(model, name): weights_name = "model_" + name +".h5" model.model.save_weights(weights_name) print("Saved model to disk") def load_model(model, name): model_name = "model_" + name + ".h5" model.load_weights(model_name) model.compile(optimizer= HP['OPTIMIZER'], loss= HP['LOSS'], metrics=HP['METRICS']) print("Loaded model from disk") return model
6 Importing Data
Importing the training and test datasets, in addition to defining the column types to be used of throughout the model.
train_df = pd.read_csv('../data/train_data_' + HP['NAME'] + '.csv', index_col=False) test_df = pd.read_csv('../data/test_data_' + HP['NAME'] + '.csv', index_col=False) data_type_dict = {'numerical': [ 'G_all', 'finalGame', 'OPS', 'SB', 'HR', 'Years_Played', 'Most Valuable Player', 'AS_games', 'Gold Glove', 'Rookie of the Year', 'World Series MVP', 'Silver Slugger', 'WHIP', 'ERA', 'KperBB', 'PO', 'A', 'E', 'DP'], 'categorical': ['HoF']}
These steps remove the labels from the data sources on both the test and training data.
### Removing the answers for the input data train_X_raw = train_df.drop(columns=['HoF']) train_y_raw = train_df['HoF'] test_X_raw = test_df.drop(columns=['HoF']) test_y_raw = test_df['HoF'] ### Converting pandas arrays to numpy arrays train_X = train_X_raw.to_numpy() test_X = test_X_raw.to_numpy() ### Creating the label data for the train and test sets encoder = LabelEncoder() train_y = encoder.fit_transform(train_y_raw) test_y = encoder.fit_transform(test_y_raw)
7 Class Weights
One of the ways of dealing with an imbalanced data set is to weight the classes. This suggestion and others are very nicely explained in this post. An error in the one class will have a much higher cost in the cost function. The following backpropagation algorithm will correct the weights based on the ratio between the class weights.
class_weights = class_weight.compute_class_weight('balanced', np.unique(train_y), train_y) class_weights = dict(enumerate(class_weights)) # class_weights = {0: 1.0, 1: 15.0} print("class weights: ", class_weights) print("value counts of Y in train_y: ", train_y.sum()) print("value counts of N in train_y: ", len(train_y) - train_y.sum())
class weights: {0: 0.5354749704375247, 1: 7.5472222222222225}
value counts of Y in train_y: 180
value counts of N in train_y: 2537
8 Grid Search for Choosing Models
A few different attempts were made to try to compare some different binary classifiers. This is mainly to keep track a backup of notes from the code. There were three different binary classifiers used. Logistic Regression seems to be the standard starting point for binary classification problems. Decisions Trees are flexible, fast, and forgiving so therefore, it was tested as a classifier. The last model was a neural network as it was hoped to be out compete the other classifiers.
- Logistic Regression
- Decision Tree and another detailed example
- Neural Network Grid Search CV, and another here.
Here are some other resources to look through for selection and comparison of different models.
- AN IN-DEPTH GUIDE TO SUPERVISED MACHINE LEARNING CLASSIFICATION
- What metrics should be used for evaluating a model on an imbalanced data set? (precision + recall or ROC=TPR+FPR)
- How to Choose a Feature Selection Method For Machine Learning
- How to Choose a Machine Learning Model – Some Guidelines
The metric used as the goal for the grid search was the Matthew Correlation Coefficient, which considers an equal weighting of false positive and false negative rates.
8.1 Decision Tree Classifier
pca = decomposition.PCA() dec_tree = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier() pipe = Pipeline(steps=[('pca', pca), ('dec_tree', dec_tree)]) n_components = list(range(1,train_X.shape[1]+1,1)) criterion = ['gini', 'entropy'] grid_scorer = make_scorer(matthews_corrcoef, greater_is_better=True) max_depth = [2,4,6,8,10,12] parameters = dict(pca__n_components=n_components, dec_tree__criterion=criterion, dec_tree__class_weight=[{0: 1.0, 1: w} for w in [10, 12, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18]], dec_tree__max_depth=max_depth) clf_GS = GridSearchCV(pipe, parameters, scoring=grid_scorer) clf_GS.fit(train_X, train_y) print('Best Score:', clf_GS.best_score_) print('Best Criterion:', clf_GS.best_estimator_.get_params()['dec_tree__criterion']) print('Best max_depth:', clf_GS.best_estimator_.get_params()['dec_tree__max_depth']) print('Best Number Of Components:', clf_GS.best_estimator_.get_params()['pca__n_components']) print(); print(clf_GS.best_estimator_.get_params()['dec_tree'])
Best Score: 0.5011699881216227
Best Criterion: entropy
Best max_depth: 8
Best Number Of Components: 22
DecisionTreeClassifier(class_weight={0: 1.0, 1: 10}, criterion='entropy',
max_depth=8)
8.2 Logistic Regression
logistic_regression = LogisticRegression(random_state=0) pipe = Pipeline(steps=[('logistic_regression', logistic_regression)]) grid_scorer = make_scorer(matthews_corrcoef, greater_is_better=True) parameters = dict(logistic_regression__penalty = ['l1', 'l2'], logistic_regression__C = np.logspace(-4, 4, 20), logistic_regression__class_weight=[{0: 1.0, 1: w} for w in [10, 12, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18]], logistic_regression__solver = ['liblinear']) clf_GS = GridSearchCV(pipe, parameters, scoring=grid_scorer, cv = 5, verbose=True, n_jobs=-1, return_train_score=True) clf_GS.fit(train_X, train_y) print('Best Score:', clf_GS.best_score_) print(); print('Best Estimator:', clf_GS.best_estimator_.get_params()['logistic_regression'])
Fitting 5 folds for each of 280 candidates, totalling 1400 fits
Best Score: 0.6192125559700654
Best Estimator: LogisticRegression(C=29.763514416313132, class_weight={0: 1.0, 1: 10},
random_state=0, solver='liblinear')
8.3 Neural Network
Some different model structures were tested for this model, but there were some 'rules of thumb' which were considered. For the number of hidden nodes in a layer:
- The number of hidden neurons should be between the size of the input layer and the size of the output layer.
- The number of hidden neurons should be 2/3 the size of the input layer, plus the size of the output layer.
- The number of hidden neurons should be less than twice the size of the input layer.
A summation of these rules were outlined as the following:
- number of hidden layers equals one
- the number of neurons in that layer is the mean of the neurons in the input and output layers.
def create_model(): model = Sequential([ Dense(26, activation='relu', input_shape=(26,)), Dense(17, activation='relu'), Dense(9, activation='relu'), Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'), ]) model.compile( optimizer= HP['OPTIMIZER'], loss= HP['LOSS'], metrics=HP['METRICS']) return model model = KerasClassifier(build_fn=create_model, verbose = 0) grid_scorer = make_scorer(matthews_corrcoef, greater_is_better=True) batch_size = [1, 2, 4] epochs = [125, 150, 200, 250, 300] param_grid = dict(batch_size=batch_size, epochs=epochs) clf_GS = GridSearchCV(model, param_grid, scoring=grid_scorer, cv = 5, n_jobs=-1) clf_GS.fit(train_X, train_y, class_weight=class_weights) print('Best Score:', clf_GS.best_score_) print(); print('Best Estimator:', clf_GS.best_estimator_.get_params())
Best Score: 0.6079706322981303
Best Estimator: {'verbose': 0, 'batch_size': 4, 'epochs': 125, 'build_fn': <function create_model at 0x7fe6b47933a0>}
9 The Final Models
Before each of these models are defined and trained, the checkpointing is set up.
These are for setting up the checkpoints while running the model. They are not really
in use right now as they are not added in the model.fit callbacks.
9.1 Decision Tree Model
# Checkpointing model_weights_name = HP['NAME'] + '_decision_tree_model.h5' checkpointer = ModelCheckpoint(model_weights_name, monitor='Recall', verbose=0) # Defining and Training the Model pca = decomposition.PCA(n_components=22) pca.fit(train_X) train_X_pca = pca.transform(train_X) test_X_pca = pca.transform(test_X) decision_tree_model = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion='entropy', max_depth=8, class_weight={0: 1.0, 1: 10.0}) decision_tree_model.fit(train_X_pca, train_y)
9.2 Logistic Regression Model
# Checkpointing model_weights_name = HP['NAME'] + '_logistic_regression_model.h5' checkpointer = ModelCheckpoint(model_weights_name, monitor='Recall', verbose=0) # Defining and Training the Model logistic_regression_model = LogisticRegression(C=29.763514416313132, class_weight={0: 1.0, 1: 10}, random_state=0, solver='liblinear') logistic_regression_model.fit(train_X, train_y)
9.3 Neural Network Model
# Checkpointing model_weights_name = HP['NAME'] + '_NN_model.h5' checkpointer = ModelCheckpoint(model_weights_name, monitor='Recall', verbose=0) # Defining and Training the Model def create_model(): model = Sequential([ Dense(26, activation='relu', input_shape=(26,)), Dense(13, activation='relu'), Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'), ]) model.compile( optimizer= HP['OPTIMIZER'], loss= HP['LOSS'], metrics=HP['METRICS']) return model nn_model = KerasClassifier(build_fn=create_model, epochs=HP['EPOCHS'], batch_size=HP['BATCH_SIZE'], verbose = 2) nn_model.fit(train_X, train_y, class_weight=class_weights, callbacks=[csv_logger, tensorboard_callback])
Epoch 1/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.3930 - accuracy: 0.8347 - recall: 0.8111 Epoch 2/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.2347 - accuracy: 0.8760 - recall: 0.9056 Epoch 3/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.2029 - accuracy: 0.8999 - recall: 0.9500 Epoch 4/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.1897 - accuracy: 0.9069 - recall: 0.9333 Epoch 5/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.1746 - accuracy: 0.9120 - recall: 0.9444 Epoch 6/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.1761 - accuracy: 0.9128 - recall: 0.9444 Epoch 7/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.1653 - accuracy: 0.9168 - recall: 0.9500 Epoch 8/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.1495 - accuracy: 0.9257 - recall: 0.9611 Epoch 9/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.1433 - accuracy: 0.9201 - recall: 0.9667 Epoch 10/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.1492 - accuracy: 0.9293 - recall: 0.9500 Epoch 11/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.1391 - accuracy: 0.9249 - recall: 0.9611 Epoch 12/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.1238 - accuracy: 0.9371 - recall: 0.9778 Epoch 13/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.1243 - accuracy: 0.9356 - recall: 0.9722 Epoch 14/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.1405 - accuracy: 0.9360 - recall: 0.9444 Epoch 15/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.1133 - accuracy: 0.9400 - recall: 0.9833 Epoch 16/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.1081 - accuracy: 0.9455 - recall: 0.9667 Epoch 17/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.1063 - accuracy: 0.9488 - recall: 0.9778 Epoch 18/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.1094 - accuracy: 0.9411 - recall: 0.9722 Epoch 19/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.0986 - accuracy: 0.9544 - recall: 0.9778 Epoch 20/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.0985 - accuracy: 0.9525 - recall: 0.9778 Epoch 21/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.0986 - accuracy: 0.9514 - recall: 0.9889 Epoch 22/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.1130 - accuracy: 0.9499 - recall: 0.9778 Epoch 23/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.0900 - accuracy: 0.9551 - recall: 0.9833 Epoch 24/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.0887 - accuracy: 0.9584 - recall: 0.9667 Epoch 25/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.0826 - accuracy: 0.9591 - recall: 0.9944 Epoch 26/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.0994 - accuracy: 0.9577 - recall: 0.9889 Epoch 27/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.0834 - accuracy: 0.9614 - recall: 0.9833 Epoch 28/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.0790 - accuracy: 0.9647 - recall: 0.9889 Epoch 29/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.0790 - accuracy: 0.9658 - recall: 0.9778 Epoch 30/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.0794 - accuracy: 0.9639 - recall: 0.9889 Epoch 31/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.0789 - accuracy: 0.9625 - recall: 0.9833 Epoch 32/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.0795 - accuracy: 0.9610 - recall: 0.9833 Epoch 33/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.0918 - accuracy: 0.9628 - recall: 0.9833 Epoch 34/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.0811 - accuracy: 0.9632 - recall: 0.9833 Epoch 35/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.0827 - accuracy: 0.9606 - recall: 0.9722 Epoch 36/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.0796 - accuracy: 0.9614 - recall: 0.9889 Epoch 37/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.0662 - accuracy: 0.9680 - recall: 0.9833 Epoch 38/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.0686 - accuracy: 0.9654 - recall: 0.9889 Epoch 39/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.0632 - accuracy: 0.9661 - recall: 0.9944 Epoch 40/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.0696 - accuracy: 0.9661 - recall: 0.9833 Epoch 41/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.0661 - accuracy: 0.9739 - recall: 0.9944 Epoch 42/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.0682 - accuracy: 0.9672 - recall: 0.9833 Epoch 43/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.0592 - accuracy: 0.9731 - recall: 0.9833 Epoch 44/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.0539 - accuracy: 0.9772 - recall: 0.9944 Epoch 45/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.0727 - accuracy: 0.9750 - recall: 0.9889 Epoch 46/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.0587 - accuracy: 0.9750 - recall: 0.9944 Epoch 47/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.0584 - accuracy: 0.9709 - recall: 1.0000 Epoch 48/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.0602 - accuracy: 0.9757 - recall: 0.9833 Epoch 49/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.0550 - accuracy: 0.9728 - recall: 0.9889 Epoch 50/50 2717/2717 - 2s - loss: 0.0742 - accuracy: 0.9713 - recall: 0.9889
10 Generating Predictions and Prediction Probabilities
The model.predict() will return the class predictions for the input data put
in the function. The model.predict_proba() will return the probability
predictions for the classes, and is the likelihood of the observation
belonging to the different classes.
# Testing the Decision Tree Model decision_tree_pred = decision_tree_model.predict(test_X_pca) decision_tree_y_score = decision_tree_model.predict_proba(test_X_pca) # Testing the Logistic Regression Model logistic_regression_pred = logistic_regression_model.predict(test_X) logistic_regression_y_score = logistic_regression_model.predict_proba(test_X) # Testing the Neural Network Model nn_pred = nn_model.predict(test_X) nn_y_score = nn_model.predict_proba(test_X, batch_size=HP['BATCH_SIZE'])
11 Metrics
Since the data set is imbalanced, there are other metrics to consider beyond
the typical accuracy. In this dataset the ratio of HoF players vs. non-HoF
players is 14:1 after preprocessing. Without class weights there could be a
bias towards never selecting the HoF players resulting an accuracy over 90%
while always predicting them as non-HoF players.
# Calculating overall metrics def print_metrics(test_y, pred, y_score, model_name): accuracy = accuracy_score(test_y, pred) mcc = matthews_corrcoef(test_y, pred) tn, fp, fn, tp = confusion_matrix(test_y, pred).ravel() confusion_mat = [tn, fp, fn, tp] auroc = roc_auc_score(test_y, y_score[:,0]) precision = tp/(tp+fp) recall = tp/(tp+fn) f1 = (2*precision*recall)/(precision+recall) # Showing numerical results confusion_label = ["tn", "fp", "fn", "tp"] for i in range(0,len(confusion_mat)): print(confusion_label[i], ': ', confusion_mat[i]) print("###### ---------Overall Results --------- ######") print("model_name: ", model_name) print("accuracy: ", accuracy) print("MCC: ", mcc) print("confusion_mat: ", confusion_mat) print("auroc: ", auroc) print("precision: ", precision) print("recall: ", recall) print("f1: ", f1) print("") # Saving the metrics metric_dict = { 'Model Name': model_name, 'True Negative': tn, 'True Positive': tp, 'False Negative': fn, 'False Positive': fp, 'AUROC': auroc, 'Accuracy': accuracy, 'Precision': precision, 'Recall': recall, 'F1': f1 } with open("../result/master_log.txt", "a") as file: print(metric_dict, file=file) print_metrics(test_y, decision_tree_pred, decision_tree_y_score, "Decision Tree") print_metrics(test_y, logistic_regression_pred, logistic_regression_y_score, "Logistic Regression") print_metrics(test_y, nn_pred, nn_y_score, "Neural Network")
tn : 576 fp : 58 fn : 22 tp : 23 ###### ---------Overall Results --------- ###### model_name: Decision Tree accuracy: 0.882179675994109 MCC: 0.3220495679851962 confusion_mat: [576, 58, 22, 23] auroc: 0.2860848229933403 precision: 0.2839506172839506 recall: 0.5111111111111111 f1: 0.3650793650793651 tn : 572 fp : 62 fn : 8 tp : 37 ###### ---------Overall Results --------- ###### model_name: Logistic Regression accuracy: 0.8969072164948454 MCC: 0.5106413422190602 confusion_mat: [572, 62, 8, 37] auroc: 0.05341745531019977 precision: 0.37373737373737376 recall: 0.8222222222222222 f1: 0.513888888888889 tn : 596 fp : 38 fn : 15 tp : 30 ###### ---------Overall Results --------- ###### model_name: Neural Network accuracy: 0.9219440353460973 MCC: 0.502772043165843 confusion_mat: [596, 38, 15, 30] auroc: 0.07173151069050122 precision: 0.4411764705882353 recall: 0.6666666666666666 f1: 0.5309734513274336
12 Plots
Three metrics that are smart to include for imbalanced datasets are:
- ROC curve
- Confusion Matrix
- Precision-Recall Matrix
# ROC curve decision_tree_fper, decision_tree_tper, thresholds = roc_curve(test_y, decision_tree_y_score[:,1]) logistic_regression_fper, logistic_regression_tper, thresholds = roc_curve(test_y, logistic_regression_y_score[:,1]) nn_fper, nn_tper, thresholds = roc_curve(test_y, nn_y_score[:,1]) plt.plot(decision_tree_fper, decision_tree_tper, color='orange', label='Decision Tree ROC') plt.plot(logistic_regression_fper, logistic_regression_tper, color='red', label='Logistic Regression ROC') plt.plot(nn_fper, nn_tper, color='green', label='Neural Network ROC') plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], color='darkblue', linestyle='--') plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate') plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate') plt.title('Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve') plt.legend() file_name = '../result/ROC_curve_' + HP['NAME'] + datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d-%H%M%S") + '.png' plt.savefig(file_name) plt.savefig("../result/ROC_curve_latest.png") plt.clf() decision_tree_man_auroc = auc(decision_tree_fper, decision_tree_tper) logistic_regression_man_auroc = auc(logistic_regression_fper, logistic_regression_tper) nn_man_auroc = auc(nn_fper, nn_tper) print("decision_tree_man_auroc: ", decision_tree_man_auroc) print("logistic_regression_man_auroc: ", logistic_regression_man_auroc) print("nn_man_auroc: ", nn_man_auroc)
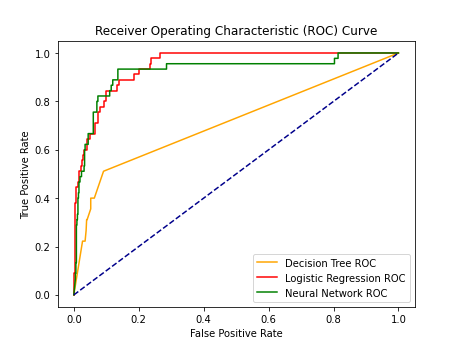
decision_tree_man_auroc: 0.7139151770066596 logistic_regression_man_auroc: 0.9465825446898002 nn_man_auroc: 0.9232211706975114
The latest ROC_plot is the following plot.
# Generating a confusion matrix def create_confusion_matrix(test_y, pred, model_name): skplt.metrics.plot_confusion_matrix(test_y, pred, normalize=True) confusion_mat_string = "../result/confusion_mat_" + HP['NAME'] + model_name + datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d-%H%M%S") + ".png" plt.savefig(confusion_mat_string) latest_model_name = "../result/confusion_mat_" + model_name + "_latest.png" plt.savefig(latest_model_name) plt.clf() create_confusion_matrix(test_y, decision_tree_pred, "decision_tree") create_confusion_matrix(test_y, logistic_regression_pred, "logistic_regression") create_confusion_matrix(test_y, nn_pred, "nn")
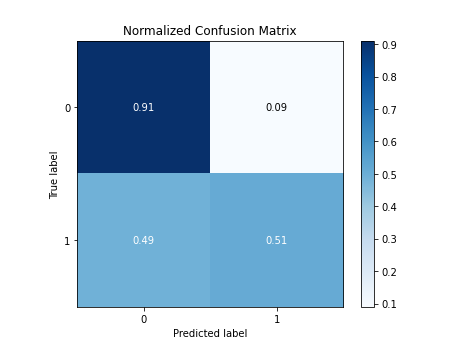
Confusion Matrix for the Decision Tree Classifier
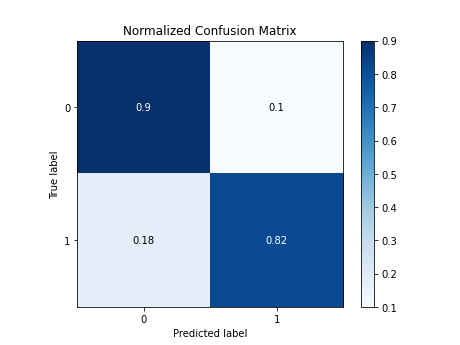
Confusion Matrix for the Logistic Regression Classifier
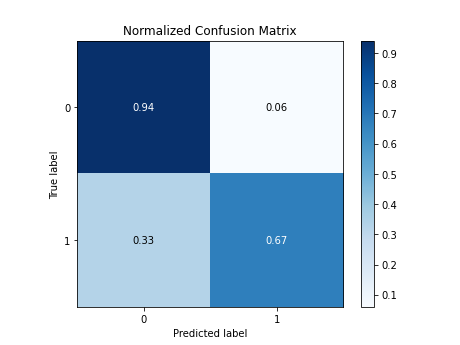
Confusion Matrix for the Neural Network Model
# Generating precision-recall curve def create_precision_recall_curve(test_y, y_score, model_name): skplt.metrics.plot_precision_recall(test_y, y_score) precision_recall_curve_string = "../result/precision_recall_curve_" + HP['NAME'] + "_" + model_name + "_" + datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d-%H%M%S") + ".png" plt.savefig(precision_recall_curve_string) latest_name = "../result/precision_recall_curve_" + model_name + "_latest.png" plt.savefig(latest_name) plt.clf() create_precision_recall_curve(test_y, decision_tree_y_score, "decision_tree") create_precision_recall_curve(test_y, logistic_regression_y_score, "logistic_regression") create_precision_recall_curve(test_y, nn_y_score, "nn")
Precision-Recall Curve for the Decision Tree Classifier
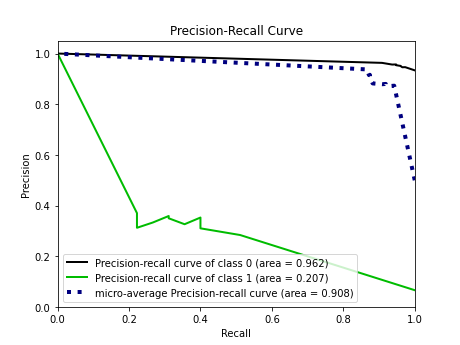
Precision-Recall Curve for the Logistic Regression
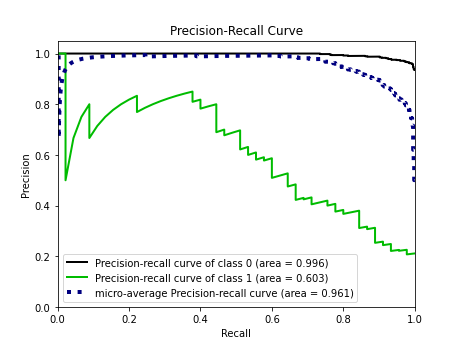
Precision-Recall Curve for the Neural Network
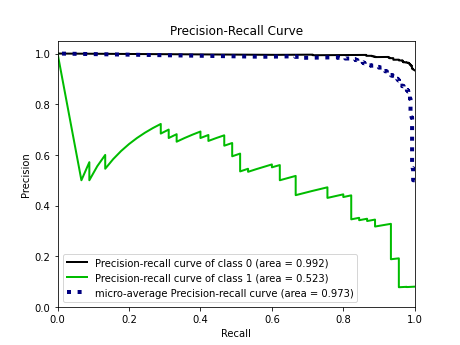
13 Links to Other Files in Project
- extract_data: Extracting data from Lahman's raw data.
- filter_data: Data manipulation, feature creation and feature selection.
- hof_model: Creation of the model and training of the neural network.
- grid_search_results: Storing some of the results for the best Grid Searches